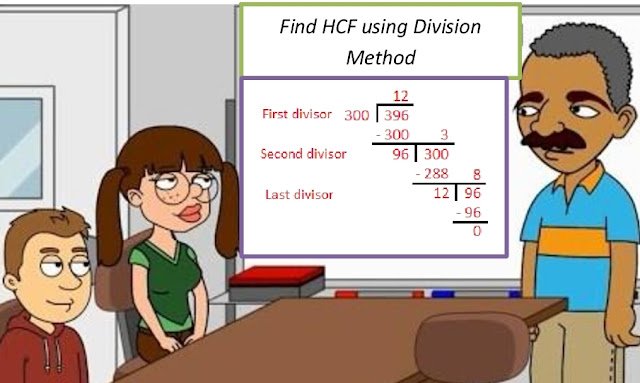
Lesson Plan of LCM Using Prime Factorization / Division Method Mathematics Grade V
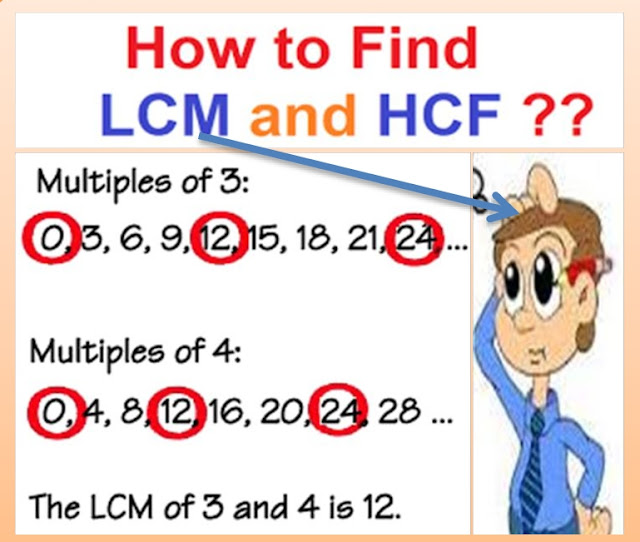
Lesson Plan of LCM Using Prime Factorization / Division Method Mathematics Grade V Students’ Learning Outcomes · Find LCM of four numbers, up to 2 digits, using prime factorization method. · Find LCM of four numbers, up to 2 digits, using division method. Information for Teacher · Since the students have done both factorization and division method for finding H CF, so they won’t find this difficult. · First go with three numbers questions and explain both methods, then individual or group work and then discuss on four numbers questions. · When any number is used to multiply with the set of natural numbers {1, 2, 3, ……}, the product of that number with each of the natural numbers is called multiples of that number, e.g. the multiples of three are : 3(1), 3(2(, 3(3), 3(4(, …. Which are respectively equal to 3, 6, 9, 12…….. · The number/multiple among the common multiples of two or more numbers is called