Lesson Plan of Separation of Insoluble Solids from Water General Science Grade IV
Lesson Plan of Separation of Insoluble Solids from Water
General Science Grade IV
Students’ Learning Outcomes
·
Predict and demonstrate how
various materials mix with water.
·
Demonstrate separation of
insoluble solids from water by decantation and filtration.
Information for Teachers
·
The substances which dissolve
in water are known as soluble substances and the resulting mixture is known as
an aqueous solution.
·
The substances which don’t
dissolve in water are termed as insoluble.
·
Insoluble solids can be
separated from the mixture by the following two method:
v Decantation is process in which upper liquid is
poured off from the settled solid.
v Filtration is a process in which insoluble
substance is separated from the mixture with the help of a filter paper.
Material / Resources
Water, sugar, glass, spoon,
common salt, chalk powder, soil, glucose, lemon juice and vinegar, textbook
Activity:
·
Ask the students: Tell
anything that is soluble in water. Get the students response and do the
following.
·
Take water in a glass. Add a
spoon full of common sugar in it and stir.
·
Ask a student to bring some
lemons then add lemon juice in a glass.
·
Inform students that this is
how we make lemon squash.
·
Inform them this is how
various materials mix with water.
·
Now mix some sand in water
and stir it. Ask students to observe. Did the sand dissolve? (No) why not? (
because sand is insoluble)
·
Can we separate the sand from
the water? (multiple responses)
·
Ask them about sieving the
tea leaves from the tea? Why do we do so? Do you know what this process is
called? Tell them that this process is called filtration.
·
Explain how filtration helps
us in daily life.
Development
Activity 1
·
Take the following three
solids. (Common salt, Sugar and Sand)
·
Ask three students to come
forward. Give each of them a glass and ask them to half fill it with water.
·
Give one of the above solids
to each student and ask them to add one spoonful of solid in water and stir it.
·
Show all the three glasses to
the whole class and ask the following questions.
v Which solid has disappeared in water?
(Students’ response: Common salt and sugar
disappear in water or they are soluble in water)
v Which solids didn’t disappear in water?
(Students’ response: Sand doesn’t disappear in
water or it is insoluble in water)
Activity 2
·
Give a student mixture of water and sand.
·
Allow the sand to settle down.
·
Ask a student to carefully decant all the water
into another glass.
·
Ask the students to name the process involved in
this activity. (Decantation)
·
Inform them that decantation can be used to
separate water from an insoluble substance with settles down.
·
Ask the students to give other examples of
decantation (Multiple responses)
Activity 3
·
Take a glass and add water
then ask student to add a spoonful of soil in the glass and stir it.
·
Let the above mixture stand
for a few minutes.
·
Ask the students:
v Have all the particles of soil settled down in
water just like the particles of sand?
(No some are still suspended)
v How can suspended particles of sand be
separated?
(Students’ response: Multiple responses) Tell
them that to separate the particles suspended in water we will use another
method called filtration.
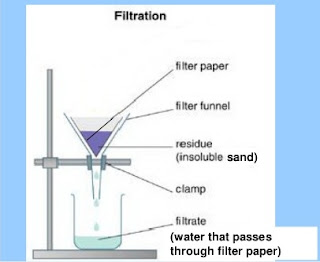
Demonstration for filtration
·
Take a filter paper. Fold it
twice to have four folds.
·
Keep three folds on one side
and one fold on the other side so that it gets the shape of a cone as shown in
the figure.
·
Moisten the filter paper with
a drop of water and fix it in the glass funnel as shown in the figure. (Size of
the filter paper should be smaller than the size of the funnel)
·
Ask a student to drop the
mixture of soil and water on the three fold side of the filter paper with the
help of a glass rod.
·
Ask students to observe and
report what happens.
·
Inform the students that
clean water will trickle down drop wise through the filter paper in the beaker
lying underneath the funnel. It is called filtrate. The soil will remain on the
filter paper. It is called the residue.
Sum up / Conclusion
·
Solids which dissolve in
water are called soluble solids.
·
Solids which don’t dissolve
in water are called insoluble solids.
·
If the particles of insoluble
solids settle down in water, they can be separated by decantation.
·
The mixture in which the
solid particles remain suspended can be separated by filtration.
Assessment
·
Write the following list of
substances on the board and ask the students to separate them as soluble or
insoluble. Sand, washing soda, ultramarine, marble pieces and glucose. Suggest a
material other than filter paper which may be used for filtration.
Substance
|
Soluble
|
Insoluble
|
Washing soda (Na2 Co3)
|
||
Sand
|
||
Ultramarine (Neel)
|
||
Marble pieces
|
||
Glucose
|
Follow up
·
Ask the students that how do
you make the water obtained from a canal free from impurities?
(Students’ response: It is
either filtered through a filter bed or through a cotton cloth).
·
Can the mixture of common
salt and water be separated by the process of decantation or filtration?







Comments
Post a Comment