Lesson Plan of Evaporation and Condensation General Science Grade V
Lesson Plan of Evaporation and Condensation
General Science Grade V
Students’ Learning Outcomes
·
Describe the role of
evaporation and condensation in the water cycle.
·
Identify and describe forms
of moisture in the environment.
(e. g. dew, snow, fog, frost
and rain)
Information for Teachers
·
When a liquid like water is
kept in an open container, its particles continuously move from liquid phase to
air. This process is called evaporation and it continues at all temperatures.
·
During night when the
temperature of air falls, the water vapours present in air get together and
form droplets of water. The process is called condensation.
·
It forms when the temperature
of an object drops below the dew point temperature. ... Frost: the ice crystals
formed by deposition of water vapor on a relatively cold ... over marshy areas
or soil saturated by a recent heavy rainfall or rapid snowmelt. ... humid air
flows over relatively cold, snow-covered ground in early spring, ...
Missing: environment
Material / Resources
Plastic
bowl, water, ice, stainless steel glass, textbook
Worm up Activity
Ask the students:
·
You must have seen your
mother spreading laundry in the open air. After some time the clothes get dry.
Where does the water go from the wet clothes? ( Students’ response: it evaporates in the presence of sunlight)
·
Ask students have you been to
a nearby garden early in the morning. Why does the grass feel wet? (Students’
response: The grass is wet due to early
morning dew)
·
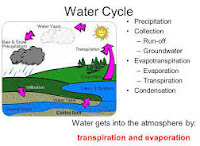
Draw this diagram on the
board and explain both the processes.
(Diagram)
Development
Activity 1
·
Take water in a bowl. Draw a
line in the bowl to indicate the level of water.
·
Ask a student to keep the
bowl in the sunlight.
·
After some time ask the
student to bring the bowl back in the classroom.
·
Let all the students observe
the level of water in the pond.
·
Ask the students the
following questions:
-----What change has occurred
in the level of water in the bowl?
( Students’ response: It has
lowered)
------Where does the water
from bowl go?
(Students’ response: It has changed into Vapours
due to heat of the Sun)
·
Explain that small drops in the
air are called water vapours. They are not visible.
Activity 2
·
Take a stainless steel glass
wipe its outer surface with dry cloth. Add some ice cubes into it.
·
After some time let the
students observe the outer surface of the glass.
-----What has appeared on the
outer surface of glass?
(Students’ response: Small droplets
of water appear on the outer surface of glass.)
------Where these droplets
have come from?
(Students’ response: Water vapours present in air, on touching the cold
surface of glass,
get together to form droplets. This process is called
condensation)
·
Teacher will inform the
students that when water vapours reach upper atmosphere they condense due to
low temperature and form clouds. Clouds cause rain.
·
Ask students to name the main
sources of water in the world?
(Students response: Sea, Lakes, Rivers, Ponds, Oceans &
atmosphere.
·
Inform students that all these
reservoirs are called water bodies.
Water moves continuously
through each of the water bodies by the processes of evaporation and
condensation and the phenomenon is called water cycle.
·
The transfer of water mainly
from oceans and other water bodies to the atmosphere takes place through
evaporation. Most water vapours return to the oceans, while some vapours are
carried by wind to different areas of land.
·
Here the vapours condense due
to low temperature and fall back on earth in the form of rain, snow and hail
and sometimes in the form of dew and fog.
·
During winter when the
morning temperature is very low, drops of water condense and suspend in the
atmosphere as fog.
·
In intense cold days these
water droplets fall down as frost. This is the way nature distributes water
throughout the land for our daily use.
Sum up / Conclusion
·
Water moves continuously
through different water bodies present on the earth by the processes of the
evaporation and condensation and the phenomenon is called water cycle.
·
Early in the morning and at
night water vapours condense together to form droplets and come down on earth
as dew or suspend in the atmosphere as fog. This process is called
condensation.
Assessment
·
Ask students the following
questions:
---How clouds are formed?
(Students response: Water vapours coming
from ocean rise up in the cooler portion of the
Atmosphere. Here they condense to form
clouds)
---What is the difference
between rain and dew?
(Students response: Water vapours present
in clouds condense together due to low temperature at high altitude).
·
Under favorable condition this
condensation causes water to precipitate as rain. At night or early in the
morning water vapours present in air condense together to form small droplets. These
droplets then fall down as dew)
----How is water present in oceans
distributed throughout the land on earth?
( Students response: Wind carries vapours present above the oceans
to far off places on earth,
where they get together at cooler
places to form clouds. These clouds then cause rain and
water is distributed throughout the
land on earth)
·
Involve the students in
solving the questions given at the end of chapter / unit of textbook,
Follow up
Ask the students to write answer
to the following questions:
-----While taking a bath during
winter with hot water what do you observe in a bathroom?
(Students response: During
bath hot water evaporate to form fog in the bath room)
-----At which times, there is
maximum possibility of the formation of dew or fog.
(Students response: Early in
the morning or during night the temperature of the
atmosphere
As fog. Alternatively heavy
droplets of water fall down in the form of dew)
------What is the name of the
process in which water vapours are converted into liquid water ?
(Students’ response: condensation)











Great but How to Stop Condensation on Windows?
ReplyDeleteSuperb hands on experience
ReplyDelete