Lesson Plan of Food Chain General Science Grade IV
Lesson Plan of Food Chain
General Science Grade IV
Students’ Learning Outcomes
·
Define producers, consumers
and decomposers and explain their importance in food chain.
·
Make a simple food chain to
show relationship among producers, consumers and decomposers.
Information for Teachers
·
Plants are called producers
because they are able to produce food (glucose) from carbon dioxide and water
in the presence of sun light.
·
Animals can’t make their own
food so they must eat plants or other animals. That’s why they called consumers.
·
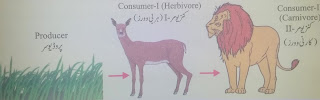
Consumers can be divided into
three groups;
v Animals that eat only plants are called
herbivores or consumer-I e.g. rabbit, sheep, goat, cow etc.
v Animals that eat other animals (herbivores) are
called carnivores or consumer-II e.g. lion, leopard etc.
v Animals that eat other animals (carnivores) are
called consumers-III e.g. snake, hawk etc.
·
Animals feed on dead body of
plants and animals and after decomposition convert them into simpler compound,
are called decomposers e.g. bacteria and fungi.
·
A food chain is the sequence
of “who eats whom” in an environment e.g.
·
Arrows represents the energy
flow in a food chain.
·
If one part of a food chain
alerts, the whole food chain is affected. For example, if a disease suddenly
wiped out butterfly caterpillars, it would affect owls, eagles and many other
animals.
Grass----------butterfly
Caterpillar ----------Owl------------Eagle
Material / Resources
Pictures of animals and plants, charts of food
chain, papers, textbook
Worm up Activity
·
Ask questions relevant to the
topic:
v From where do we get our food?
v Why do we need food?
v What do plants and animals get their food?
v From where do animals get their food?
v From where do plants get their food?
v How we, animals and plants are related to each
other?
·
To make food chain, draw
relation among plants, animals and man e.g.
Plants --------------- Cow
-----------------Man
Development
Activity 1
·
Demonstrate some examples of
simple food chains.
·
Introduce the concept of
plants as producers i.e. organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis.
·
Introduce the concept of
animals as consumers i.e. organisms that eat producers or other consumers.
·
Explain the role of
decomposers in all food chains.
·
Ask students to make a food
chain by making a sequence of the following organisms. The students will also
mention the producer and the consumers.
Activity 2
 ·
Introduce a complex food
chain i.e. with more than one consumer. Categorize the consumers as consumer-
I, II, III and so on.
·
Introduce a complex food
chain i.e. with more than one consumer. Categorize the consumers as consumer-
I, II, III and so on.Activity 3
·
Reinforce the learning of food
chain through the following role-play:
v Write the word producer, herbivore,
carnivore-I, carnivore-II and carnivore-III on a separate paper.
v Give one paper to each student.
v Whatever the paper says, that becomes the
student’s role in the food chain.
v Paste the paper to their backs.
v Herbivore tries to catch the producer. When a
producer gets tagged the two students link arms.
v Carnivore-I tries to catch the herbivore and
when he / she is successful, they link arms.
v Carnivore-II tries to catch the carnivore –I and
when he / she is successful, they link arms.
v Similarly, carnivore-III tries to catch the
carnivore-II and when he is successful, they link arms.
·
Ask students to draw the
developed food chain on paper.
Sum up / Conclusion
·
Each living thing, whether it
is a plant or animal, depends on nutrients and energy to survive.
·
Food chain tells us how the
food is passed from organism to organism.
·
All food chains start with
plants that make their own food. These are called producers.
·
Next come organisms that eat
plants. These organisms are called consumer-I and we know that they are herbivores.
·
Then come the animals that
eat herbivores. These are called consumer-II and we know that they are
carnivores.
·
In all food chains; when any
organism dies, it is eaten and broken down by decomposers. Some bacteria and
fungi are decomposers.
Assessment
Activity 1
·
Ask students to make
corrections in the following food chain
Activity 2
·
Make a table on the board and
ask students to copy the table on their note books.
Consumer-II
|
Organism that feeds on
plants
|
Consumer-I
|
Order in which food passes
from one living thing to another
|
Producer
|
Break down the dead body of
animals and plants
|
Food chain
|
Living organism that is
capable of manufacturing its food
|
Decomposer
|
Organism that eats animals
|
Activity 3
·
Ask students to make a
correct sequence of plants and animals in the following activities (or the
similar ones). If pictures are not available, write the names of these
organisms on the board.
Follow up
·
Ask students to complete the
food chains by filling in the blank boxes with the correct consumers or
producers given in the underneath food chains.
Food chain 1:
Grasshopper, Grass, Hawk,
Snake, Rat
Food chain 2:
Birds, Cat, Snail, Grass
algae
Food chain 3:
Grass, Fox, Rabbit, Bear
Types of organisms
|
Food chain 1
|
Food chain 2
|
Food chain 3
|
Producer
|
|||
Consumer –I
|
|||
Consumer-II
|
|||
Consumer-III
|
·
Ask the students to separate
different food chains in the following diagram.








Comments
Post a Comment