Lesson Plan of Atomic Structure and Isotopes General Science Grade VII
Lesson Plan of Atomic Structure and Isotopes
General Science Grade VII
Students’ Learning Outcomes
·
Describe the structure of an
atom.
·
Define the term isotopes.
·
Explain uses of isotopes in
medicines and agriculture.
Information for Teacher
·
Atoms are the smallest
particle of an element.
·
An atom is the simple form of
an element that can take part in a chemical reaction.
·
Atoms are basic building
blocks of matter.
·
The word atom is derived from
the Greek word atom which means indivisible.
·
Atoms are composed of three
types of particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
·
Protons have a positive (+)
charge, neutrons are neutral while electrons have a negative charge (-)
·
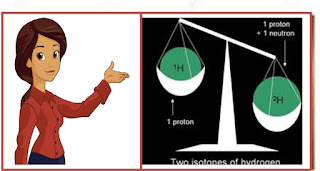
Atoms of a given element
which have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are
called isotopes. Thus, isotopes of an element have same chemical properties but
different physical properties.
·
Isotopes are often used in
medical research and therapy for a variety of diseases and genetic disorders.
·
Isotopes are mostly used in
various uses in medicine, to diagnose and treat illnesses.
·
They are also used widely in
biochemical research in various fields like chemistry, physics, neurosciences and
biology.
Concept Map
Material / Resources
A ball made of plasticize, different colored
marbles or stone (chocolate bun ties can also be used) glue, small rosary
beads,
Worm up activity
·
Teacher can start the lesson
by asking what is everything made of? Every building, every person, every
object? (Students will answer matter and atoms). They can be taught about
atomic structure by using following activity:
Activity
·
Teacher can now explain
structure of atom by showing children the model of hydrogen atom made from ball
and marbles.
·
·
In the model the ball may be
depicted as the nucleus of the atoms.
·
The marbles of orange color
will represent protons. Put these in the nucleus. There are no neutrons in a
hydrogen atom.
·
Use a bendable wire to make
the orbital and add rosary beads. Ask children to keep on rotating the beads to
show movement of electrons. Leave 2 inches distance between nucleus and
electrons.
·
Teacher should explain about
the different types of charges on electrons and protons.
·
Teacher should explain
children that electrons are always moving. They spin very quickly and in any
direction around the nucleus.
·
Draw following pictures on
board to give the spin and orbital concept.
Development
Activity 1
·
Teacher can divide the class
in three groups and ask children to make models of carbon and helium atom.
·
Teacher will write the
following data on board.
·
Carbon: 6 protons, 6 neutrons
and 6 electrons.
·
Helium: 2 protons, 2 neutrons
and 2 electrons.
·
Instructions should be given
to children that electrons are present around the nucleus in shells. Shells or
orbitals serve as home of electrons.
·
First shell can have two
electrons. 2nd shell can have 8 electrons and third can have up to 18
electrons.
·
Move around the class and
assist children in making models. Also ask them questions like where will be
the protons, what will be their charge.
·
Ask both groups to come for a
presentation and explain their atomic models.
·
The models should look have
the arrangement given below.
Activity 2
·
Teacher can draw the
following diagram on board.
·
Img
·
Ask the children to identify the
four parts of the atom that are pointed out by arrows in the diagram above.
·
Describe the electrical
charges of the structures that are labeled 1, 2, and 3 in the diagram.
(Expected response: Number 1
is the electrons, 2 is the proton, 3 is the neutron, and 4 is the nucleus).
Charges: the electron is negative, proton is positive and neutron is neutral.
Activity 3
·
Teacher can explain students
what are isotopes and where are they used. To strengthen their concepts more,
she can tell that
·
Colbat-60 is used in food
preservation. It is also used to sterilize medical equipment (e.g. gloves,
syringes, cotton balls, etc.) as it produces gamma radiations.
·
Medical isotopes are also
used in treatment and diagnosis of diseases.
·
Show students the following
picture and ask to explain the process.
·
After listening to their explanations
tell them that using radiations produced by isotopes is a method of treating
food in order to make it safer to eat.
·
Tell them that this method is
also used to export fruits and vegetables to other countries as food life is
increased.
·
Students can be asked to
prepare a list of other processes where isotopes can be used.
Sum up / Conclusion
·
Teacher may conclude the
lesson by telling children that they have learnt.
·
An atom has subatomic particles
called protons, neutrons, electrons.
·
Protons have positive charge,
electrons have negative while neutrons have no charge.
·
Isotopes are of great medical
and industrial use.
Assessment
·
Teacher may ask some
questions at the end of the lesson to ensure that they now know:
o
What is the position of electrons, protons and
neutron in the structure of any atom?
o
What are types of charge on electrons and
protons and neutrons?
o
Define the term isotopes.
o
What are uses of isotopes in food and medicine
industry?
Follow up
·
Show students the following
picture of destruction in japan caused by an isotope of hydrogen.
Tell them the
interesting fact that all new clocks and watches made in japan have the same
time 10:10 as bomb was dropped at this time. It is in the memory of those who
died in Hiroshima Nagasaki nuclear attack. Ask them to find out which isotope
of hydrogen was used for it?








This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete