LESSON PLAN OF THE PRONOUN AND ITS KINDS
LESSON NO. 17 THE PRONOUN AND ITS KINDS
Subject English
Grade 10th
THE PRONOUN
- Pronoun is a word that is used instead of a noun or noun-equivalent. Pronoun is made of two words: Pro- means for. So pronoun means ‘for a noun’. Pronoun is used to avoid repetition of noun, as such;
1. Adnan is a good boy. He studies at a private college. He is liked by his teachers. His class fellows respect him.
KINDS OF PRONOUN
- There are ten different kinds of pronouns:
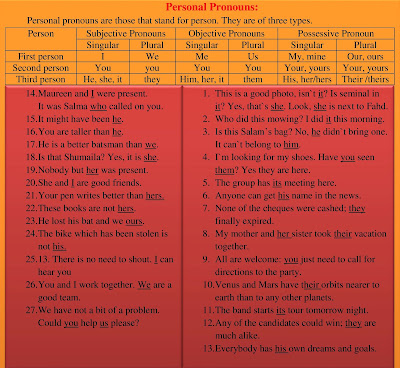
(1) Personal Pronouns:
- Personal pronouns are those that stand for person. They are of three types.
|
Person |
Subjective
Pronouns |
Objective
Pronouns |
Possessive
Pronoun |
|
|||
|
Singular |
Plural |
Singular |
Plural |
Singular |
Plural |
|
|
|
First
person |
I |
We |
Me |
Us |
My,
mine |
Our,
ours |
|
|
Second
person |
You |
you |
You |
You |
Your,
yours |
Your,
yours |
|
|
Third
person |
He,
she, it |
they |
Him,
her, it |
them |
His,
her/hers |
Their
/theirs |
|
1. Maureen and I were present. It was Salma who called on you.
2. It might have been he.
3. You are taller than he.
4. He is a better batsman than we.
5. Is that Shumaila? Yes, it is she.
6. Nobody but her was present.
7. She and I are good friends.
8. Your pen writes better than hers.
9. These books are not hers.
10. He lost his bat and we ours.
11. The bike which has been stolen is not his.
12. 13. There is no need to shout. I can hear you
13. You and I work together. We are a good team.
14. We have not a bit of a problem. Could you help us please?
15. This is a good photo, isn`t it? Is seminal in it? Yes, that`s she. Look, she is next to Fahd.
16. Who did this mowing? I did it this morning.
17. Is this Salam’s bag? No, he didn`t bring one. It can`t belong to him.
18. I`m looking for my shoes. Have you seen them? Yes they are here.
19. The group has its meeting here.
20. Anyone can get his name in the news.
21. None of the cheques were cashed; they finally expired.
22. My mother and her sister took their vacation together.
23. All are welcome: you just need to call for directions to the party.
24. Venus and Mars have their orbits nearer to earth than to any other planets.
25. The band starts its tour tomorrow night.
26. Any of the candidates could win; they are much alike.
27. Everybody has his own dreams and goals.
(2) Reflexive Pronouns:
- When-self is added to my, him, her, your, and –selves is added to our, your, them, we get what are called Reflexive pronouns. Reflexive pronouns are used when the action done by the subject turns back (reflects) upon the subject, as such;
1. I hurt myself.
2. She hurt herself.
3. They hurt themselves.
4. You hurt yourself/yourselves
5. He hurt himself.
6. I saw myself in the mirror.
7. He himself will be our new friend.
(1) Relative Pronouns:
- Relative pronoun is a pronoun that joins two statements. It therefore does the work of a conjunction. But unlike conjunction the Relative pronouns refer or relate to some noun going before which is called Antecedent, as such; who, whose, whom, which, that,
1. I met all who had just arrived.
2. I found my pen which I had lost.
3. Salem is my student who stood first in the class.
4. Here is the book that you want.
5. It is love that completes me to help you.
6. I have an ox whose legs are long.
7. The sun, whose rays give life to things, is regarded by some people as a god.
8. He is the man who saved my life.
9. He is the boy whose father is a lawyer.
10. She is the girl whom I met in Lahore.
11. The story, which appeared in the daily Dawn, was written by Aslam.
12. This is the only thing that I can do for you.
(1) Distributive Pronouns:
- Each, either, neither, any are called Distributive Pronouns because they refer to persons or things one at a time. For this reason, they are always singular and are followed by the verb in the singular, as such;
1. Each boy was given a prize.
2. Each day is different.
3. Either road leads to the station.
4. Either girl can do that.
5. Neither accusation is true.
6. Neither answer is correct.
7. None of the three girls are present.
8. You can take any of the shirts.
9. We invited many people but none come.
10. Each of the answers is correct.
11. Neither of the boys true.
12. Either of the ways goes to masjid.
(5) Indefinite Pronouns:
- A pronoun that refers to persons or things in general is called indefinite pronoun. But they don`t refer to any person or thing in particular, as such; one, any, some, all, none, nobody, everyone, neither, either, each, nothing are indefinite pronouns.
1. One hardly knows what to do.
2. None of his poems is impressive.
3. All were present.
4. Some say he is a teacher.
5. Nobody was there.
6. The last couple of years have been a long bumpy ride for me, as they have for every one of my age.
7. Everybody enjoys a good movie.
8. Does anybody have the time?
9. One sang while the other played the guitar.
10. Nobody knows the trouble I’ve seen.
11. The secret was known by few.
12. No, the secret was known by many.
13. Mathematics is too hard for some.
14. Surely, you recognize somebody.
15. Is there anything that I can do?
16. Each of the family members has one vote.
17. One of the boys eats pizza every week.
18. Both of the answers are correct.
(1) Demonstrative Pronouns:
- Demonstrate pronouns are used to point out the objects to which they refer, as such; this, these (refers to things that are near), that, those (refers to what is over there, far away) are demonstrative pronouns.
1. This is a car that I want to buy.
2. These are things that you need.
3. That is your brother.
4. Those are your friends.
(7) Interrogative Pronouns:
- Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions, as such; who, whose, whom, which, what are interrogative pronouns;
1. Who is there?
2. Who are you?
3. What do you want?
4. Which is the house?
5. What will all the people say?











Comments
Post a Comment